Market research is a systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including data about potential customers, competitors, and the industry.
It is essential for small businesses because it helps in understanding customer needs, identifying new market opportunities, and making informed business decisions.
Conducting effective market research can lead to improved products, better customer service, and a stronger market position.
How to Do Market Research for Small Business and Its Examples
Types of Market Research
Primary Research:
This involves collecting new data directly from the source. Examples include:
- Surveys: Structured questionnaires distributed online or in-person to collect quantitative data on consumer behavior, preferences, and demographics. Example: “How often do you purchase organic products?”
- Interviews: One-on-one discussions, either face-to-face or via phone/video, to gather in-depth qualitative insights into customer opinions and experiences. Example: “Can you describe your last experience with our product?”
- Focus Groups: Small, diverse groups of people discussing a topic guided by a moderator to uncover attitudes and perceptions. Example: Gathering a group of frequent shoppers to discuss their shopping habits.
Secondary Research:
This involves analyzing existing data that has already been collected by other sources. Examples include:
- Industry Reports: Publications by market research firms that provide comprehensive analysis on industry trends, market size, and growth forecasts. Example: A report on the growth of the organic food market.
- Market Statistics: Data from governmental or commercial sources that provide quantitative information about the market. Example: Census data on consumer demographics.
- Existing Studies: Research papers, articles, and previous surveys that offer insights into market trends and consumer behavior. Example: Academic papers on consumer behavior in the digital age.
Additional Examples of Secondary Research Sources:
- Trade Associations: Organizations like the National Retail Federation (NRF) provide industry-specific data and reports.
- Market Research Databases: Platforms such as Euromonitor International and Mintel offer detailed market analysis and consumer insights.
- Academic Journals: Access to databases like JSTOR or Google Scholar for peer-reviewed research papers.
- News Outlets: Business sections of major newspapers (e.g., The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg) often provide market analysis and industry news.
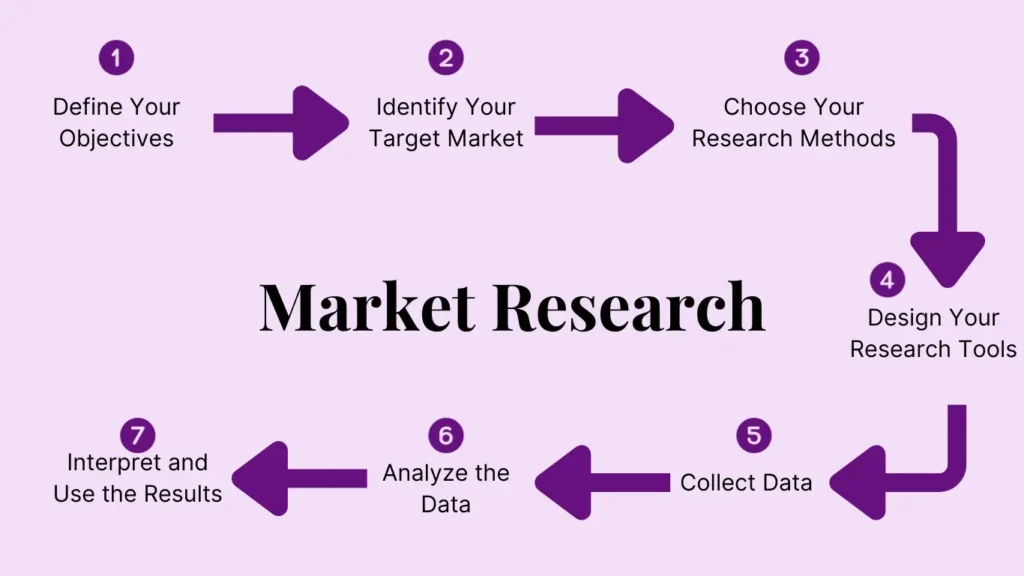
Steps to Conduct Market Research for Small Business
1- Define Your Objectives:
Clearly state the goals of your research. This could include understanding customer preferences, evaluating the market size, identifying potential competitors, or assessing the feasibility of a new product.
- Example Objective: Determine the most desired features for a new fitness app.
2- Identify Your Target Market:
Identify your target market by defining your ideal customer profile by considering:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, education level, occupation.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, values, interests, attitudes.
- Behavior: Buying habits, brand loyalty, product usage.
- Example: Targeting health-conscious millennials aged 25-35 who live in urban areas.
3- Choose Your Research Methods:
Decide your research method between qualitative methods (interviews, focus groups) and quantitative methods (surveys, data analysis). Each method has its strengths:
- Surveys: Ideal for gathering large amounts of data quickly and statistically analyzing trends.
- Interviews: Best for gaining a deeper understanding of individual customer experiences.
- Focus Groups: Useful for exploring new ideas and gathering diverse opinions.
- Example: An online survey will be used to gather feedback on app features, and a focus group will be used to discuss user experiences in detail.
4- Design Your Research Tools:
Create effective tools for data collection:
- Surveys: Ensure questions are clear, concise, and unbiased. Use a mix of multiple-choice, rating scale, and open-ended questions.
- Interviews: Prepare a set of open-ended questions to guide the discussion, but be flexible to explore interesting points raised by interviewees.
- Observation: Develop a checklist of behaviors or actions to observe in a natural setting.
- Example: Survey question: “On a scale of 1 to 10, how satisfied are you with our current product features?”
5- Collect Data:
Utilize various data collection methods and tools:
- Online Survey Platforms: SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, Typeform.
- Social Media Analytics: Tools like Hootsuite or Sprout Social to gather insights from social media platforms.
- In-person Methods: Direct interviews, focus groups, and observations.
- Example: Conducting an online survey through Google Forms and using Hootsuite to analyze social media discussions about fitness apps.
6- Analyze the Data:
Organize and interpret the collected data:
- Quantitative Analysis: Use statistical methods to identify patterns and trends. Tools like Excel or SPSS can help analyze survey data.
- Qualitative Analysis: Identify themes and insights from interviews and focus groups. Tools like NVivo can assist in coding and analyzing qualitative data.
- Example: Analyzing survey results to find that 70% of respondents prefer features related to workout tracking.
7- Interpret and Use the Results:
Draw actionable insights from the analysis:
- Identify Key Findings: Summarize the most important insights and trends.
- Develop Action Plans: Use the insights to make informed business decisions, such as product improvements, marketing strategies, or new market entry.
- Example: Deciding to focus on enhancing workout tracking features based on survey feedback.
Example of Market Research for Small Business
Example of Local Bakery’s Flavor Survey
A local bakery was looking to expand its product line to attract more customers and increase sales.
The bakery decided to use market research to identify which new flavors would be most popular among its customers.
Methods Used:
- Surveys: The bakery created an online survey using Google Forms and distributed it through their email newsletter and social media channels. The survey included multiple-choice questions about preferred flavors and open-ended questions for additional suggestions.
- In-store Feedback: They also placed suggestion boxes in their stores, encouraging customers to write down their favorite flavors and any new ones they would like to see.
Key Findings:
- 60% of respondents expressed a preference for gluten-free options.
- Among gluten-free options, chocolate and almond flavors were the most requested.
- Many customers suggested the addition of vegan options as well.
Impact on Business Metrics:
- Product Launch: The bakery introduced a new line of gluten-free and vegan pastries, including chocolate and almond flavors.
- Sales Increase: Within three months of launching the new product line, the bakery saw a 20% increase in overall sales.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer feedback post-launch indicated a high level of satisfaction, with many praising the taste and variety of the new offerings.
By using surveys and in-store feedback, the bakery successfully identified and met customer demand, resulting in increased sales and improved customer satisfaction.
Tools and Resources
- Online Survey Tools:
- SurveyMonkey: A popular tool for creating and distributing surveys.
- Google Forms: A free tool integrated with Google Drive, easy to use for simple surveys.
- Typeform: Known for its engaging and interactive survey designs.
- Analytics Tools:
- Google Analytics: Provides insights into website traffic and user behavior.
- Hootsuite: A social media management tool that offers analytics on social media engagement.
- HubSpot: Offers marketing analytics and reporting tools.
- Industry Reports and Databases:
- Statista: Provides market and consumer data across various industries.
- IBISWorld: Offers detailed industry reports and analysis.
- Government Databases: Sources like the U.S. Census Bureau for demographic data.
- Trade Associations: Organizations such as the American Marketing Association (AMA) and the National Retail Federation (NRF) provide industry-specific data and insights.
- Market Research Databases: Platforms like Euromonitor International, Mintel, and Nielsen offer comprehensive market analysis and consumer insights.
- Academic Journals: Databases like JSTOR or Google Scholar for access to peer-reviewed research papers.
- News Outlets: Business sections of major newspapers (e.g., The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg) often provide market analysis and industry news.
Cost Considerations
- Surveys: Online tools like Google Forms are free, while others like SurveyMonkey offer tiered pricing based on features. In-person surveys can incur costs related to printing and distribution.
- Interviews: Generally low-cost but can become expensive if compensating participants for their time. Consider using video conferencing tools to reduce travel costs.
- Focus Groups: Costs include participant incentives, venue rental, and potentially hiring a professional moderator. Online focus groups can reduce some of these costs.
- Secondary Research: Free sources include government databases and some academic journals. Subscription-based services like Statista, Euromonitor, and IBISWorld can be costly but provide comprehensive data.
Budget Tips:
- Leverage Free Tools: Utilize free versions of survey tools and social media analytics.
- DIY Methods: Conduct interviews and focus groups yourself if possible, rather than hiring external help.
- Use Existing Data: Start with secondary research to gather background information before investing in primary research.
Additional Methods
- Ethnographic Research: Involves observing customers in their natural environment to understand their behaviors and needs. Example: Observing how customers use a product in their homes.
- A/B Testing: Comparing two versions of a product or marketing material to see which performs better. Example: Testing two different website layouts to see which leads to more conversions.
- Competitive Analysis: Studying competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Example: Analyzing a competitor’s marketing strategies and customer reviews.
Follow-Up Actions
After interpreting the data, implement specific follow-up actions:
- Strategic Planning: Use insights to shape your business strategy, including market positioning and long-term goals. Example: Deciding to enter a new market segment based on identified opportunities.
- Marketing Adjustments: Tailor your marketing campaigns to better reach and engage your target audience. Example: Launching a social media campaign focused on the features most desired by your customers.
- Product Development: Modify or develop new products based on customer feedback and market needs. Example: Adding a highly requested feature to your app or introducing a new product line.
Tips for Effective Market Research
- Stay Objective: Maintain impartiality to avoid biases that could skew results. Use randomized sampling and avoid leading questions.
- Keep it Ongoing: Market research should be a continuous effort to keep up with changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
- Be Cost-Effective: Utilize free or low-cost tools and resources where possible. Consider leveraging existing data before conducting new research.
- Engage with Customers: Regular interactions with customers can provide valuable insights. Encourage feedback through various channels, including social media, email, and in-person.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Bias in Research: Ensure diverse and representative samples to avoid skewed data. Randomize your sample selection and use neutral wording in questions.
- Overlooking Secondary Research: Don’t ignore the wealth of existing information that can provide valuable context and save time. Start with secondary research before moving to primary research.
- Misinterpreting Data: Take care to accurately analyze data and draw valid conclusions. Avoid jumping to conclusions based on insufficient or anecdotal evidence.
Market research for small businesses is essential to understand their market, meet customer needs, and stay competitive. By following the outlined steps and utilizing the provided tools and examples, you can conduct effective market research that drives your business success.
Additional Resources
- “Marketing Research Kit For Dummies” by Michael Hyman and Jeremy Sierra: A comprehensive guide for beginners.
- “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries: Offers insights on how to use market feedback to drive business growth.




